Network redundancy is your digital infrastructure's insurance policy. It is the technical practice of duplicating critical network components, connections, and data pathways to ensure business continuity when hardware fails or a link goes down. For any business dependent on its IT infrastructure, it's not a luxury—it's a foundational requirement for survival.
What Is Network Redundancy and Why It Matters
At its core, network redundancy is a strategy to eliminate Single Points of Failure (SPOFs). It applies the same logic as a backup generator: you build a parallel system that can take over instantly, ensuring that a single component failure doesn't cause a catastrophic outage. This involves creating alternate data pathways and duplicating key hardware like routers, switches, servers, and even power supplies.
This isn't just a technical exercise; it's a critical business strategy. Every minute your systems are offline costs money, erodes customer trust, and sends clients searching for more reliable alternatives. If you've ever been frustrated trying to figure out why your WiFi keeps disconnecting, imagine that disruption scaled across your entire business. When a bare metal server, virtual machine, or primary internet connection fails, the impact is immediate and severe.
The True Cost of a Single Point of Failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is any component in your system whose failure will take down the entire operation. It could be a single internet connection, an un-clustered firewall, or a standalone server running a critical application. The primary goal of network redundancy is to systematically identify and eliminate these weak links. By ensuring no single component can halt your operations, you build a fault-tolerant and highly available system.
The demand for this level of resilience is surging. The global Network Redundancy Providers market is projected to reach $42.7 billion by 2033, signaling a clear industry-wide mandate for uninterrupted operations. Investing in redundancy is no longer a "nice-to-have"—it's a baseline for modern business. You can explore more details on the growth of the network redundancy market at htfmarketinsights.com.
For businesses running on ARPHost’s VPS hosting or dedicated Proxmox private clouds, our built-in redundancy is what keeps applications responsive, payments processing, and data flowing without interruption.
Core Principles of Network Redundancy at a Glance
To implement redundancy effectively, it helps to understand its fundamental goals. The table below outlines the key principles that form the foundation of any robust, redundant network architecture.
| Principle | Objective | Key Components Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Fault Tolerance | Maintain system operation even after one or more components fail. | Routers, Switches, Firewalls, Power Supplies, Servers. |
| High Availability | Maximize uptime and ensure services are consistently accessible to users. | Multiple Internet Service Providers (ISPs), Clustered Servers, Load Balancers. |
| Reliability | Deliver consistent and predictable network performance over time. | Redundant Cabling, Automated Failover Protocols, Backup Data Paths. |
| Disaster Recovery | Recover quickly from a catastrophic failure or site-wide outage. | Geographically separate data centers, Off-site backups. |
Ultimately, these principles work in concert to create a network that is resilient, dependable, and prepared for unexpected failures. They are the building blocks of a system designed not just to survive an outage, but to operate as if it never occurred.
Peeling Back the Layers of Network Redundancy
Defining network redundancy is the first step, but a true implementation requires a multi-layered strategy, not a single fix. Each layer is designed to address a different potential point of failure, working together to build a truly resilient infrastructure. Think of it like building a secure fortress: you need a strong outer wall, a deep moat, and vigilant guards—a complete, integrated defense.
A comprehensive redundancy plan must account for everything from a failed power supply on a server to a regional internet outage. By breaking the system down into distinct layers, we can methodically identify and eliminate vulnerabilities.
This diagram illustrates the two primary areas of focus: physical hardware (components) and data routes (pathways).
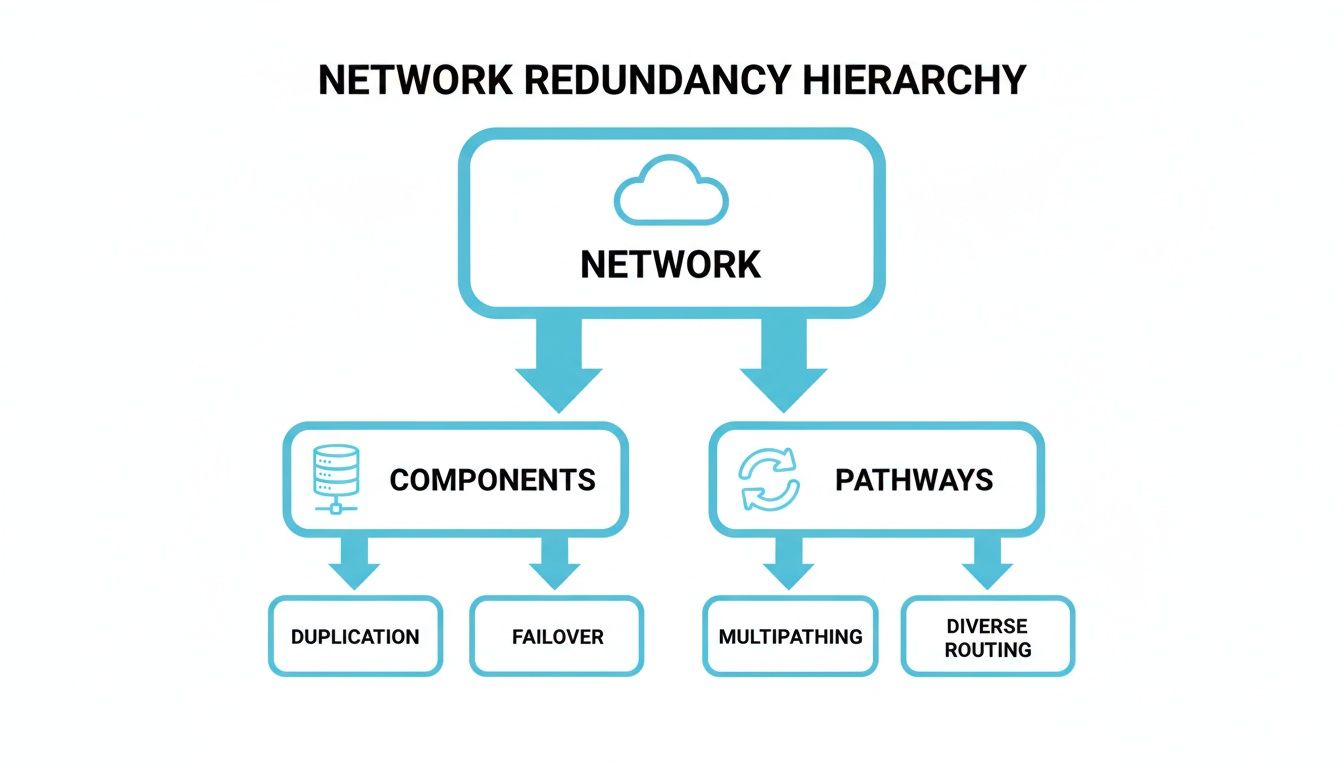
As shown, a complete strategy must address both hardware and connectivity. Neglecting one leaves your entire system exposed.
Device Redundancy
Device redundancy protects against the failure of a single piece of hardware. This is the foundation of your fortress. The goal is to have a duplicate for any critical network appliance so its failure doesn't halt operations.
Common technical examples include:
- Dual Firewalls in HA Pair: A primary firewall actively manages traffic, while a secondary, passive firewall stands by, ready to take over instantly if the primary fails. This is a best practice in secure network design, often managed as part of ARPHost's Managed IT Services.
- Redundant Power Supplies (PSUs): Mission-critical bare metal servers and network switches almost always feature two PSUs, each connected to a separate power circuit. If one circuit fails or a PSU dies, the device continues running without interruption.
- Clustered Servers: In a virtualized environment like a Proxmox private cloud, multiple physical servers (nodes) work as a single entity. If a node fails, virtual machines (VMs) running on it are automatically and seamlessly migrated to a healthy node in the cluster. This is the core of high-availability virtualization.
Link and Path Redundancy
While device redundancy secures your hardware, link and path redundancy protects your connection to the outside world. A link is the physical connection, such as a fiber optic cable from an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The path is the logical route your data takes across one or more links.
Imagine having two separate roads to your office. Having two roads is link redundancy. Using an alternate route when the first is blocked by traffic is path redundancy.
In networking, this typically means contracting with at least two different ISPs. If one provider experiences an outage, your network's edge router automatically reroutes all traffic through the secondary provider's link. For any business that relies on constant connectivity, this is a non-negotiable requirement.
Key Takeaway: Link redundancy provides the alternate physical connections. Path redundancy provides the automated intelligence to use them when a failure occurs. Both are essential for a bulletproof internet connection.
Site Redundancy
Site redundancy is the ultimate layer of protection, guarding against large-scale disasters like regional power failures, natural disasters, or any event that could incapacitate an entire data center. It involves duplicating your entire IT infrastructure in a geographically separate location.
If your primary data center is compromised, you can fail over all operations to your secondary site. This is the cornerstone of a robust disaster recovery plan. For businesses seeking maximum uptime, leveraging a carrier-neutral data center like ARPHost's is crucial, as it provides the diverse connectivity options needed for a solid multi-site strategy.
Active-Active vs. Active-Passive Setups
When implementing these layers, you will encounter two primary configuration models: Active-Active and Active-Passive.
- Active-Passive: This is the traditional failover model. One component (the "active" one) handles 100% of the workload while its identical counterpart (the "passive" one) remains on standby. The passive unit only activates if the active one fails. It's a reliable and cost-effective approach.
- Active-Active: In this configuration, both components are online and processing traffic simultaneously. This not only provides failover protection but also enhances performance by load-balancing the work between them, effectively doubling capacity. This high-performance configuration is ideal for demanding applications and is a common setup in our Dedicated Proxmox Private Clouds.
The choice depends on your budget, performance requirements, and the criticality of the system. Active-Passive offers solid protection, while Active-Active delivers both protection and a significant performance boost.
The Protocols That Power Automatic Failover
How does a network switch from a failed path to a backup in milliseconds without human intervention? The answer lies in a set of sophisticated networking protocols designed specifically to automate failover and maintain constant connectivity. These protocols are the unsung heroes of network redundancy, providing the intelligence that transforms a collection of backup hardware into a resilient, self-healing system.
Without them, a redundant architecture is just expensive, unused equipment waiting for an engineer to manually intervene during a crisis.

VRRP for Router and Gateway Redundancy
One of the most common SPOFs is the default gateway—the router that directs traffic out of your local network. The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) solves this by creating a "virtual" router from a group of two or more physical routers. One router is elected the "master" and handles traffic, while the others act as "backups." If the master fails, a backup router instantly takes its place, assuming the master role and the virtual IP address. To your servers and devices, the failover is completely transparent.
This ensures the virtual gateway IP address remains online, keeping traffic flowing. ARPHost's managed network services implement protocols like VRRP on enterprise-grade Juniper hardware to provide this essential layer of gateway protection for our clients.
LACP for Bundling Physical Links
What happens if a single network cable is unplugged or a switch port fails? The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) prevents this from causing an outage by bundling multiple physical network cables into a single, logical high-bandwidth connection.
This technique, also known as port-channeling or bonding, provides two key benefits:
- Increased Bandwidth: Bundling four 1Gbps links creates a single logical 4Gbps pipe.
- Fault Tolerance: If one physical link in the bundle fails, traffic is automatically redistributed across the remaining links with zero interruption.
LACP is fundamental to building resilient connections between switches, servers, and storage, ensuring no single cable can disrupt service. You'll find this implemented by default in our Proxmox Private Cloud environments.
STP for Preventing Network Loops
In a redundant network with multiple switches and paths, there's a risk of creating a network loop, where data packets circle endlessly, consuming all available bandwidth and crashing the network. The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is the classic technology that prevents this.
STP intelligently maps the network topology and blocks redundant paths to create a single, loop-free route. However, it keeps those blocked paths on standby. If the primary path fails, STP automatically unblocks a backup path to restore connectivity.
While essential, STP requires careful configuration. As part of our fully managed IT services for servers, ARPHost engineers meticulously tune STP to ensure you get the benefits of redundant paths without the risk of crippling network loops.
BGP for Multi-Homed Internet Connectivity
For true path redundancy, you need connections from more than one Internet Service Provider (ISP). The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the core routing protocol of the internet. By using BGP, your network can:
- Announce its own IP addresses to multiple ISPs simultaneously.
- Receive routes from all connected providers.
- Intelligently select the best and fastest path for outbound traffic.
If your primary ISP has an outage, BGP automatically detects the failure and reroutes all traffic through your secondary provider. This is the cornerstone of a multi-homed internet strategy, providing the ultimate resilience against provider outages.
The hardware that enables these protocols, such as redundancy switches, is a critical component of modern infrastructure. This technology is powering a market projected to hit $1.98 billion by 2033, driven by the intense demands of cloud computing and data center expansion. For ARPHost clients using our bare metal servers and VPS hosting, this underscores the industry-wide commitment to the unbreakable uptime these protocols deliver. You can explore more about the market trends for this crucial hardware on datainsightsmarket.com.
How to Design Your Redundant Network Strategy
Moving from theory to a resilient, production-ready network requires more than just buying duplicate hardware. It demands a methodical plan to build a system that is resilient by design. The process starts with a thorough audit of your current infrastructure to identify every potential weak link. From there, you can make informed decisions that balance the cost of implementation against the tangible risks of downtime.
Identify Every Single Point of Failure
Your first task is to conduct a comprehensive audit to identify every Single Point of Failure (SPOF). Map your entire infrastructure—from physical hardware to logical connections—and identify every component whose failure would cause an outage.
Ask critical questions:
- Hardware: What happens if our primary firewall fails? Do our mission-critical servers have redundant power supplies connected to separate power distribution units (PDUs)?
- Connectivity: What is our plan if our sole internet provider has a regional outage? Is a single core switch connecting all our servers?
- Services: If our primary DNS server goes offline, can clients resolve our domain? What about our authentication server or Virtual PBX phone system?
This audit provides a clear, actionable list of vulnerabilities to address.
Conduct a Risk vs. Cost Analysis
Not every system requires the same level of protection. A development server can tolerate some downtime, but your e-commerce platform cannot. This is where a risk vs. cost analysis is essential. For each identified SPOF, weigh the business impact of its failure against the cost of implementing a redundant solution.
Calculate the cost of one hour of downtime, factoring in lost revenue, lost productivity, and brand damage. Compare this figure to the cost of a redundant solution. For example, adding a second internet connection and a managed firewall might cost a few hundred dollars per month. If an outage would cost thousands per hour, the decision is clear. This analysis ensures your budget is allocated to protecting your most valuable assets.
Pro Tip: An active-active, geographically redundant setup for a non-critical internal tool is likely overkill. Conversely, relying on a single server for a revenue-generating application is an unacceptable risk. Your analysis should guide you to the appropriate level of redundancy for each system.
The Critical Importance of Testing
A failover system that has never been tested is not a system; it's a liability. The final and most crucial step is to proactively test your redundant configurations. You must simulate failures to verify that your automatic failover mechanisms perform as expected.
Schedule regular maintenance windows to conduct these tests:
- Unplug the primary network link to a critical server. Does traffic seamlessly fail over to the secondary link via LACP?
- Power down the active firewall in your HA pair. Does the passive unit take over without dropping active connections?
- Simulate a server failure in a cluster. Do the virtual machines automatically migrate to another node? You can see how this works in our guide to Proxmox High Availability.
These controlled tests are the only way to identify and resolve issues before a real outage occurs. An untested redundancy plan provides a false sense of security, which is often more dangerous than having no plan at all.
Building a Resilient Business with ARPHost
Understanding the theory of network redundancy is one thing; implementing it with battle-tested infrastructure is another. At ARPHost, we don't just provide hosting—we deliver a foundation of resilience engineered to keep your business online. Our services are designed to eliminate single points of failure, transforming redundancy from a complex challenge into a tangible business advantage.
We build redundancy into every layer of our solutions, from high-availability VPS plans to fully managed private clouds. This allows you to focus on your business, confident that your digital operations are protected by a robust and reliable infrastructure.

High-Availability VPS with Self-Healing Storage
For most businesses, a server failure is a crisis. Our High-Availability VPS Hosting plans are engineered to prevent this. Built on the KVM hypervisor and backed by a distributed CEPH storage system, our VPS environment is self-healing. If a physical server node fails, your virtual machine is automatically and instantly migrated to a healthy node in the cluster with zero data loss.
This architecture provides built-in device and link redundancy out of the box, keeping your websites and applications online without manual intervention. It’s enterprise-grade resilience made accessible, with plans starting at just $5.99 per month.
Dedicated Proxmox Private Clouds
When your applications demand maximum performance and complete isolation, a Dedicated Proxmox Private Cloud from ARPHost is your ideal solution. We build custom clusters on dedicated bare metal servers, creating a private, high-availability environment exclusively for your workloads.
Here’s how we engineer it for near-100% uptime:
- Clustered Compute Nodes: Multiple physical servers work in unison. If one fails, your virtual machines are automatically restarted on healthy nodes.
- Redundant Networking: We use enterprise-grade Juniper networking hardware with bonded network interfaces (LACP) and redundant switch paths to eliminate any network-level single points of failure.
- Distributed Storage: With CEPH, your data is replicated across multiple physical drives and servers, protecting you from both individual disk failures and entire server outages.
This provides a complete, multi-layered redundancy strategy that you control with full root access, all supported by our 24/7 expert management.
Colocation for Geographic Redundancy
For the ultimate layer of protection, you need site redundancy. ARPHost's colocation services allow you to place your own hardware in our secure, carrier-neutral data center. This is the key to building a geographically diverse infrastructure and establishing a secondary site for disaster recovery. By duplicating your critical systems at our facility, you can fail over your entire operation if your primary site goes down. It is an essential component of any serious disaster recovery plan. For more information, see our guide on what is disaster recovery planning.
Why ARPHost Excels Here
A truly resilient infrastructure is more than just duplicate hardware. It requires expert configuration, constant monitoring, and support that never sleeps. Our fully managed IT services become an extension of your team, handling the complex setup of failover protocols, security patching, and monitoring. We use enterprise-grade Juniper networking and provide 24/7 access to experts who live and breathe high-availability environments. You get a battle-tested infrastructure without the operational nightmare.
Tying redundancy challenges directly to ARPHost solutions can clarify how we help businesses stay online. This table breaks down common problems and shows which of our services is the best fit.
ARPHost Solutions for Network Redundancy Challenges
| Redundancy Challenge | Recommended ARPHost Solution | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Preventing single server failure for websites or apps. | High-Availability VPS Hosting | Automatic, instant failover to a healthy node with self-healing storage. |
| Needing total control and isolation for critical applications. | Dedicated Proxmox Private Cloud | A fully isolated, multi-layered redundant environment with full root access. |
| Protecting against a primary site disaster like a power outage or natural disaster. | Colocation Services | Establishes a geographically separate disaster recovery site. |
| Lacking in-house expertise to manage complex HA setups. | Fully Managed IT Services | 24/7 expert management of failover, security, and monitoring. |
Our goal is to make these powerful strategies accessible, so you can build a resilient business without needing a massive IT department.
The investment in this kind of robust infrastructure is clearly paying off for businesses everywhere. For instance, the market for PLC redundancy—a similar concept in the industrial world—was valued at $411.17 million in 2024 and is projected to grow. This shows a clear ROI that businesses in manufacturing, e-commerce, and IT see from slashing downtime.
After all, a primary benefit of network redundancy is ensuring high uptime, which is crucial for keeping customers happy and operations running smoothly. Discover more insights about these market trends on 360iResearch.com.
A Few Common Questions About Network Redundancy
When planning for network resilience, several key questions often arise. Here are straightforward answers to help you make informed decisions about your infrastructure.
What's the Real Difference Between Redundancy and High Availability?
These terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. The simplest way to understand it is: redundancy is the method, while high availability is the goal.
- Redundancy is the practice of duplicating critical components—servers, routers, network links—to eliminate single points of failure. It is your "plan B."
- High Availability (HA) is the outcome of a well-designed, redundant system. It is a measurement of system uptime, typically expressed as a percentage like 99.999% ("five nines").
You implement redundancy to achieve high availability. For example, ARPHost's High-Availability VPS Hosting uses redundant physical servers and self-healing CEPH storage (the redundancy) to ensure your virtual machine remains operational even if underlying hardware fails (the high availability).
Seriously, How Much Redundancy Do I Need?
The right level of redundancy depends entirely on your specific business requirements and risk tolerance. It's about balancing cost against the impact of an outage.
To determine your needs, ask these questions:
- What does an hour of downtime cost me? For an e-commerce store, every minute offline means lost revenue. For a development server, the impact is minimal.
- What are my RTO/RPO targets? Your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is how quickly you must recover, and your Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is how much data you can afford to lose. Mission-critical applications require near-zero RTO and RPO.
- What's my budget? Start by protecting your most critical systems and addressing the most obvious single points of failure first.
A simple business website may only need a secure web hosting bundle with reliable automated backups. A complex financial application, however, will likely require a fully redundant Dedicated Proxmox Private Cloud to maintain compliance and continuous operation.
Is High Uptime Possible on a Tight Budget?
Absolutely. Achieving high uptime is no longer exclusive to large enterprises with massive budgets. Thanks to modern virtualization and strategic planning, robust resilience is accessible to businesses of all sizes. The key is to focus on solutions that offer the greatest return on investment.
It's a common myth that true resilience is prohibitively expensive. With today's virtualization and storage tech, you can get enterprise-grade uptime for less than the cost of a daily cup of coffee.
Here are a few budget-friendly strategies:
- Use Managed HA Services: Instead of purchasing and managing duplicate hardware yourself, leverage a service built for high availability. ARPHost’s KVM-based High-Availability VPS plans start at just $5.99/month and handle failover automatically.
- Be Strategic with Duplication: You don't need two of everything. Identify your most critical SPOFs—such as your primary web server or database—and focus your initial investment there.
- Leverage Cloud-Based Backups: A solid backup and disaster recovery plan is a form of redundancy. Secure, off-site backups ensure you can recover from a catastrophic failure without needing a fully mirrored data center.
By choosing the right tools and partners, you can build a resilient infrastructure that protects your business without breaking your budget.
At ARPHost, we engineer resilience into everything we do, from our self-healing VPS clusters to our fully managed private clouds. Let our experts help you build a redundant, high-availability infrastructure that fits your goals and your budget.
Check out our powerful and affordable High-Availability VPS Hosting plans to get started today.


